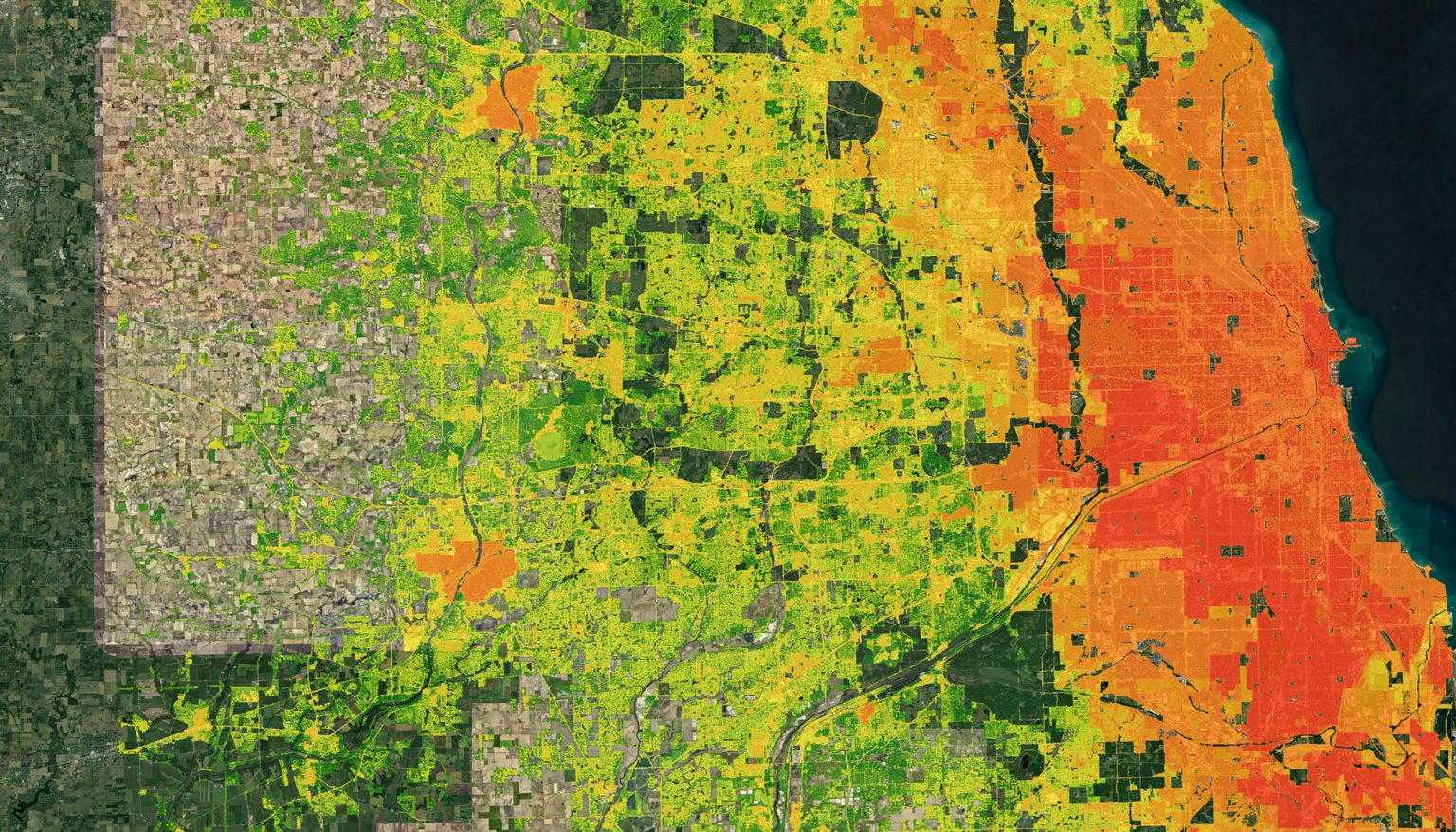
In today’s rapidly evolving technological landscape, businesses and governments are increasingly leveraging the synergy between geospatial mapping and big data. This powerful combination allows organizations to analyze vast amounts of location-based information, uncover patterns, and make informed decisions with unprecedented accuracy.
Understanding Geospatial Mapping
Geospatial mapping involves the visualization of data in a geographic context. It enables users to plot data points on maps, revealing spatial relationships and trends that might otherwise go unnoticed. Traditionally used in fields like urban planning, transportation, and environmental monitoring, geospatial mapping has now become integral to many industries thanks to advances in data analytics.
The Role of Big Data
Big data refers to extremely large datasets that cannot be processed using traditional methods. These datasets often come from diverse sources, including social media, sensors, satellites, and transactional records. When analyzed effectively, big data provides deep insights into customer behavior, operational efficiency, and market trends.
How Geospatial Mapping and Big Data Work Together
Combining geospatial mapping and big data transforms raw information into actionable intelligence. For example:
- Urban Planning: City planners can use geospatial analytics on traffic and population data to design smarter infrastructure.
- Disaster Management: Real-time satellite data combined with big data analytics allows for faster response during natural disasters.
- Retail and Marketing: Businesses can analyze customer locations and shopping behaviors to optimize store placements and marketing strategies.
This combination not only enhances decision-making but also provides predictive insights that help organizations stay ahead of trends.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite its potential, integrating geospatial mapping with big data comes with challenges. Data privacy, accuracy, and integration from multiple sources require careful attention. Additionally, processing such massive datasets demands robust computing infrastructure and specialized analytical tools.
Conclusion
The fusion of geospatial mapping and big data represents a powerful combination that is reshaping industries worldwide. By turning location-based data into actionable insights, organizations can improve efficiency, respond quickly to challenges, and make strategic decisions with confidence. As technology continues to advance, this combination will only become more vital for achieving competitive advantage.